DISTRACTION OSTEOGENESIS
Distraction osteogenesis, an innovative surgical method pioneered by Russian orthopedic surgeon Gavriil Ilizarov in the 1950s, entails the gradual adjustment or elongation of bones. Rooted in the concept that bones can regenerate under tension, this technique commences with a precise bone cut and the attachment of a distraction device using screws or pins. The device is then slowly turned, creating a 1-millimeter separation of bone fragments daily. This process spans weeks or months until the desired bone lengthening or repositioning is attained.

This procedure, with applications ranging from limb lengthening to craniofacial reconstruction, non-union treatment, and joint replacement, boasts several advantages. These include minimal scarring, reduced infection risk, precise control over the lengthening process, and minimal reliance on bone grafting.
Distraction osteogenesis has transformed the landscape of bone deformity treatment, providing a less invasive and more controlled approach to bone adjustment. Whether addressing shorter-than-normal limbs, reconstructing craniofacial bones affected by injuries or birth defects, treating non-unions, or facilitating joint implants, this versatile technique stands as an effective solution.
Facial disharmony can range in terms of form, size and shape of tooth and/ or jaws. Functional disharmony creates inability to chew, speak properly and can potentially interfere with normal breathing process. Aesthetic aspect includes loss of self-confidence and social isolation.
The treatment of children with facial deformities has advanced at a rapid pace over the past two decades. Keeping pace with recent global trends, our Hospital offers advances in medicine and technology to attain perfect results. Dr. S.M. Balaji’s expertise is at the forefront in the field of craniofacial anomaly surgery.
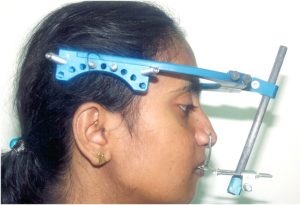
Distraction Osteogenesis is an innovative treatment option in cranio-maxillo-facial surgery. It is a means of stimulating production of new bone. In this procedure, the jaw bone is cut and the two arms of the distractor device are attached to the cut bone segments. After a few days the distraction procedure is started. The screw attached to the device is turned gradually (1 mm per day) which pushes the bones apart. New bone is formed in the resultant gap. After the desired jaw bone length is achieved, distraction is stopped. Once the new bone stabilizes, the distractor device is removed.
This cutting edge technology allows lengthening of the jaw without the formation of scars as the technique is approached from within the mouth.
Distraction is the magical technique by which we can achieve bone growth in childhood, early or even late adulthood. This technique is a boon to those who have bone growth retardation and to those who have lost some of their bone tissue to tumors or trauma. The versatility of this technique lies in the fact that corrections can be achieved more precisely even to the last millimeter.
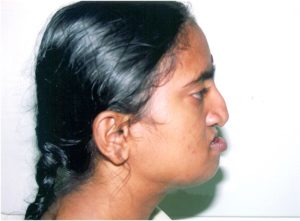
Micrognathia
A child’s lower jaw may sometimes be comparatively undersized than the upper jaw. This condition is termed as Micrognathia. The growth of muscles would also be simultaneously affected as the bony structure is smaller than normal. This condition could also be associated with various syndromes (Pierre-Robin’s Syndrome, Treacher Collin’s Syndrome etc). As the lower jaw is small, the tongue gets pushed backwards and tends to block the air passage.
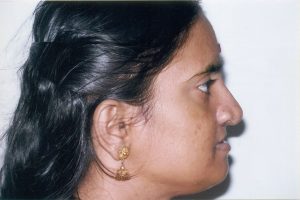
Distraction Osteogenesis is an effective treatment option to lengthen the jaw size. By this procedure the jaw can be brought to the normal size, without the necessity of bone grafting (bone harvested from hip bone to lengthen the jaw size).
Hemifacial Microsomia
In some individuals, there may be an imbalance between right and left sides of the face. This type of facial growth deformity characterized by facial asymmetry is called Hemifacial Microsomia. In this condition, the structures of one side of the face grow lesser than the other side. This results in asymmetry of the face. The affected side of the face appears disproportionately smaller than the other. The commonly affected structures of this deformity are the lower jaw, eyes, ears, facial nerve and the cheeks. The most significant defect is that of the jaws, which when corrected, minimizes the entire deformity and makes the face look almost symmetric.
The best and most advanced treatment technique of reconstructive jaw surgery for facial asymmetry is Distraction Osteogenesis. Our hospital remains the only center till date in this part of the world to offer simultaneous Distraction Osteogenesis (Distraction of both upper and lower jaw) for the correction of facial asymmetries and has successfully rehabilitated the maximum number of patients afflicted with facial disfigurements in the country.
Facial bone deficiency or Hypoplasia can be corrected by bone grown by distraction. The asymmetry of the face that occurs due to lack of growth on one side of the face can be set right by “Simultaneous Maxillary and Mandibular Distraction”
Advantages of Distraction osteogenesis
- Distraction osteogenesis is a safe and precise technique to correct the bone defect. The amount of deformity as assessed by specialized X-rays can be corrected to millimeter precision.
- Second surgery to harvest bone for bone grafting is avoided.
- The results are stable and permanent with no relapse to the original size.
- Distraction can be performed in three dimensions i.e. advancing, widening and increasing vertical height of the jaws.
- Skin, muscles, nerves and vascular tissues are generated, not stretched, therefore along with the underlying bone deformity, the overlying skin and soft tissue defect is also corrected.
- It can be used to simultaneously correct deformities of both upper and lower jaw.
- It is the only procedure to increase the size of the jaw bones after the cessation of actual bone growth.
Uses of Distraction
Distraction osteogenesis can be used to lengthen the lower jaw. It also finds uses in the following:
- Correcting anterior-posterior deformity of the jaws
- Trauma reconstruction
- Cancer reconstruction
- Craniofacial syndromes
- To widen the jaws to correct teeth crowding
- Asymmetry corrections
- Increasing bone width and height of teeth bearing region of upper or lower jaw for dental implants
- Previously failed bone graft sites
- When available donor bone is insufficient
- When patient is not an ideal candidate for bone grafting