What is Crouzon syndrome?
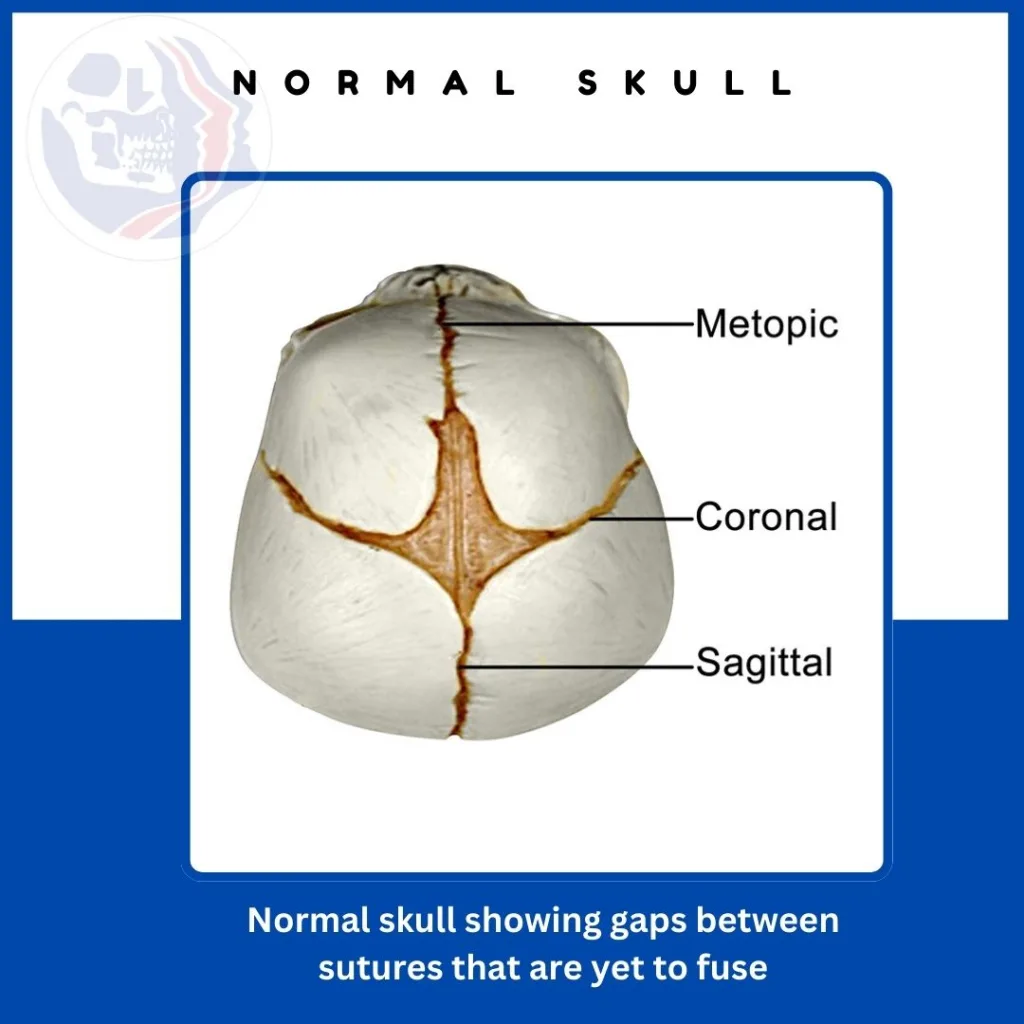
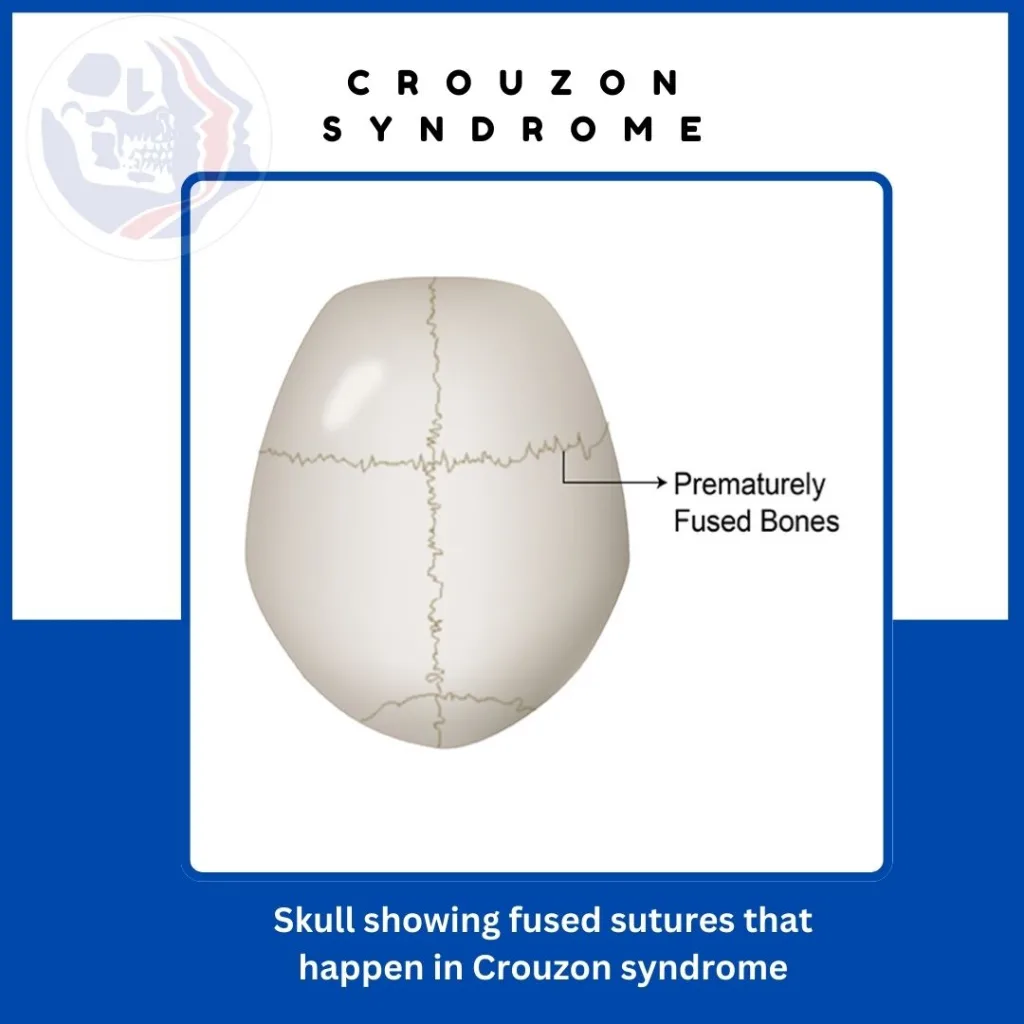
Crouzon syndrome is a rare genetic disorder in which the gaps or sutures between the bones are fused. In this condition the sutures of skull bone are closed prematurely. This leads to an abnormal growth pattern resulting in an unusually shaped skull.
This early fusion of skull bones is called craniosynostosis. This hinders the normal growth of the skull, affecting the shape of the head and face. The eyes appear to bulge out, and jaws and the middle face are sunken in appearance, leading to craniofacial abnormalities.
Why does Crouzon syndrome occur?
Crouzon syndrome is an autosomal dominant disorder that occurs due to mutations in the FGFR2 (fibroblast growth factor receptor 2) gene. The FGFR2 gene is responsible for giving signals that help in normal bone growth. . This mutation affects the development of the skull and facial bones.
Any mutations of this gene can disrupt the normal signaling pathways involved in bone growth and development, leading to premature fusion of bones. This syndrome is mostly inherited, but it can occur due to spontaneous gene mutations as well.
Incidence of Crouzon Syndrome
Globally, Crouzon disease occurs in approximately 1 in 25,000 live births, with cases increasingly being recognized and treated in India due to advancements in genetic testing and craniofacial care.
Any mutations of this gene can disrupt the normal signaling pathways involved in bone growth and development, leading to premature fusion of bones. This syndrome is mostly inherited, but it can occur due to spontaneous gene mutations as well.
