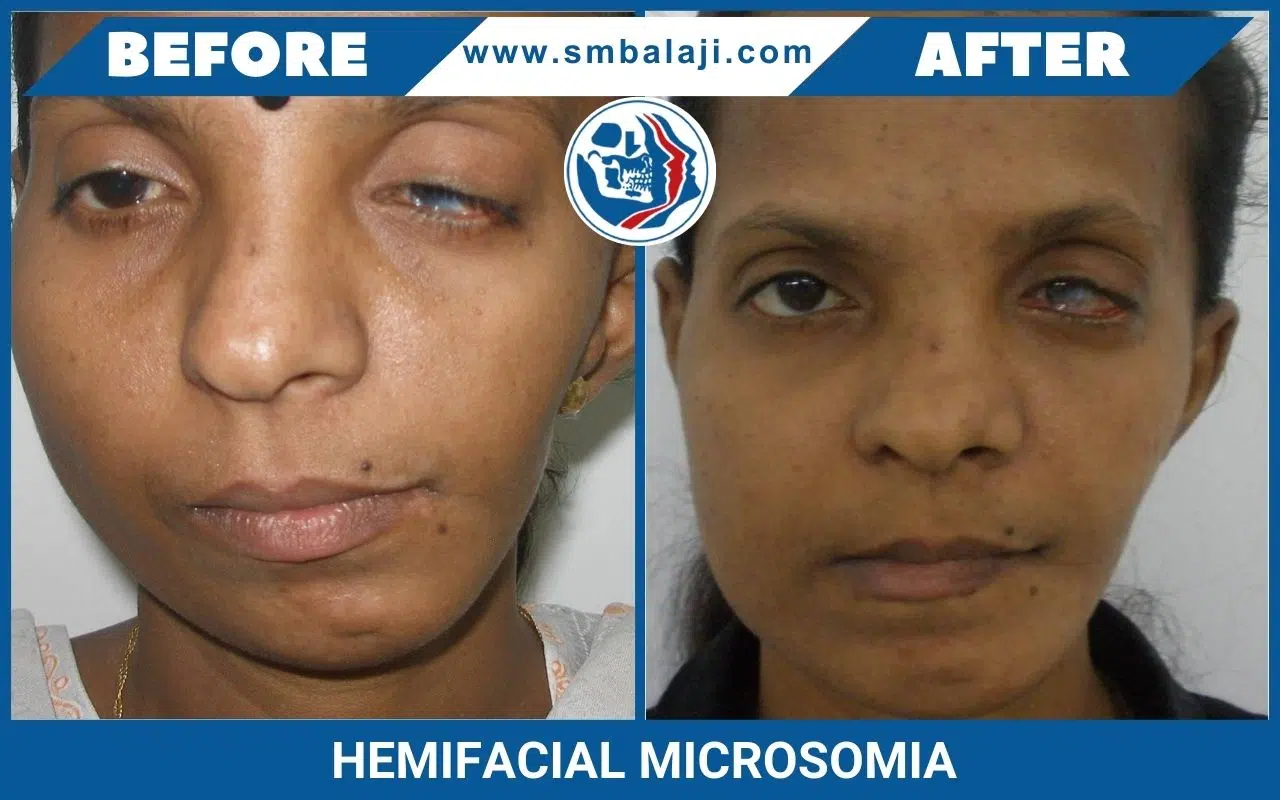
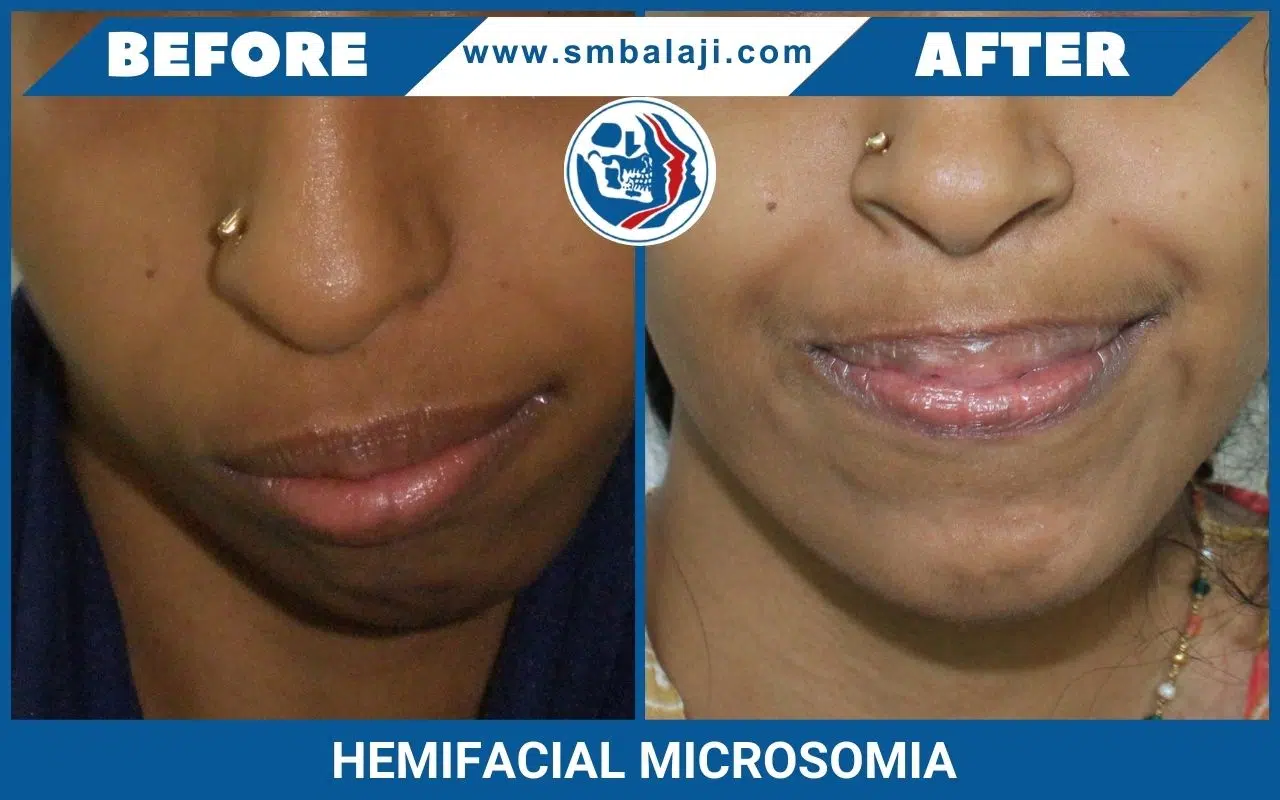
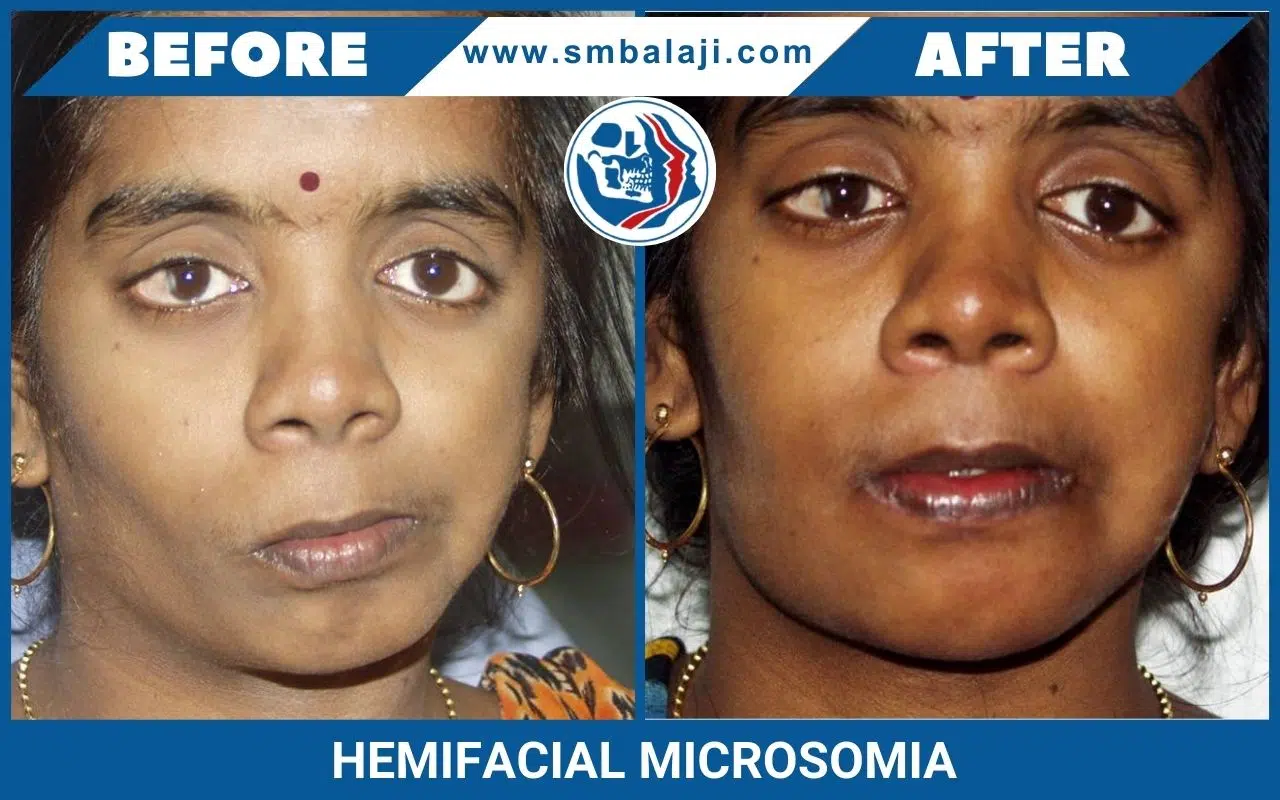
HEMIFACIAL MICROSOMIA
Discover comprehensive care for Hemifacial Microsomia (HFM), also recognized as Craniofacial Microsomia or Goldenhar Syndrome, at Balaji Dental and Craniofacial Hospital. This congenital disorder affects the lower half of the face, primarily impacting the ears, mouth, and mandible, often appearing unilaterally but occasionally affecting both sides.
Characteristics of Hemifacial Microsomia:
HFM’s severity varies, with some individuals displaying mild abnormalities and others experiencing more pronounced deformities. Common features include:
- Underdeveloped jaw (mandible) on one side
- Smaller or absent ear on one side
- Facial asymmetry
- Missing or deformed cheekbone
- Cleft lip or palate
- Eyelid abnormalities
- Hearing loss
Causes of Hemifacial Microsomia:
While the exact cause remains unknown, HFM is thought to result from a blend of genetic and environmental factors. Research suggests a potential link to disruptions in blood flow during facial development in pregnancy.
Diagnosis of Hemifacial Microsomia:
Typically diagnosed at birth or shortly after, a doctor’s physical examination is often sufficient. Confirmatory imaging, such as X-rays or CT scans, may be employed to assess the extent of deformities.
Treatment Options for Hemifacial Microsomia:
Individualized treatment is tailored to the deformity severity and may include:
- Surgery: Common for reconstructing the jaw, ear, and facial structures.
- Speech Therapy: Aiding children in developing normal speech patterns.
- Hearing Aids: Beneficial for those with hearing loss.
- Psychological Counseling: Assisting both children and adults in coping with emotional and social challenges.
Prognosis for Hemifacial Microsomia:
Prognosis varies based on deformity severity. With treatment, most individuals can lead normal and productive lives.

What is Hemifacial Microsomia
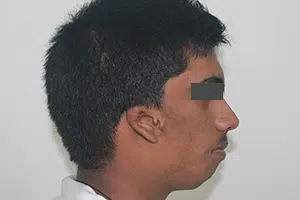
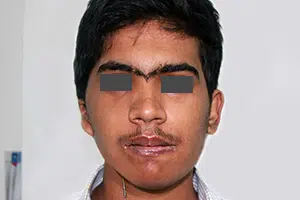
Hemifacial Microsomia is a birth deformity affecting the bony skeleton and soft tissues of the craniofacial region. It is typically characterized by pronounced asymmetry of the face due to deficient growth of the lower jaw (mandible) on one side, deficient soft tissues of the face and underdeveloped ear (microtia).
Bony and soft tissue structures on one side of the face grow lesser than the other side. The affected side of the face appears disproportionately smaller than the other. Commonly affected are the lower jaw, eye, ear, facial nerve and cheek. The most significant of these deformities is that of the jaws, which when corrected, minimizes the entire deformity and makes the face look more symmetric.
In hemifacial microsomia, the shape and size of the lower jaw is deformed on one side causing an asymmetric face. The chin appears deviated to the affected side. Facial asymmetry progresses as the patient grows. As a result, teeth bite (occlusion) is slanted.
Treatment
Based on various parameters like severity of the defect and age of the patient, there are different treatment options. Cheek and eye socket bone defects if present, can be corrected with specialized craniofacial surgeries. Ear and soft tissue defects can be rehabilitated with reconstructive surgeries.
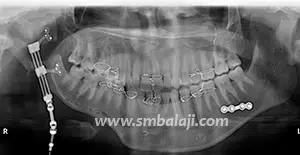
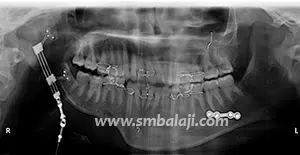
Distraction Osteogenesis
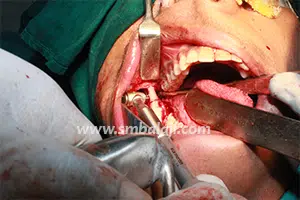
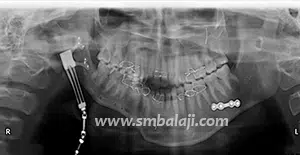
The goal of treatment in hemifacial microsomia is to elongate the deficient jaw bone to restore facial symmetry and correct the slanting bite (occlusion). To achieve this, an advanced and effective treatment technique is distraction osteogenesis. This is a new technique for regenerating new bone by slow, progressive stretching of the bone, without requiring a bone graft.
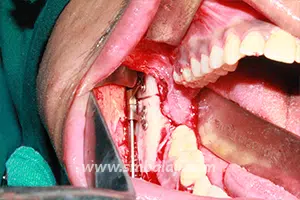
The jaw bone on the deficient side is cut. A sophisticated device called distractor is placed such that the two arms of the device are fixed to the two segments of jaw bone. After a few days, a screw attached to the distractor is turned gradually, ideally at a rate of 1 mm per day. When this is done, the two cut segments move apart and new bone is formed in the resultant gap. After the new bone is stabilized, the distractor device is removed.
Subsequently, the jaw bone is lengthened to the desired amount correcting the asymmetry of the face. This is a powerful tissue engineering technique for generating unlimited bone.
Eminent Facio-Maxillary Surgeon Dr. S.M. Balaji is highly acclaimed for his prowess in the treatment of Hemifacial Microsomia. He is a pioneering expert in this field and has applied several revolutionary techniques including “Simultaneous Maxillary and Mandibular Distraction” giving excellent results to set right facial asymmetry.
Our hospital has to its credit the maximum number of cases of Hemifacial Microsomia successfully treated with Distraction Osteogenesis (Distraction of both upper and lower jaw) for the correction of facial asymmetries.